Remote computer control
With Advanced EDR, you can remotely connect to the computers on your network from the web console to check their status or start troubleshooting tasks.
Remote access tools included in Advanced EDR
-
Remote control terminal: Remote shell that enables you to perform administrator operations on the file system and run programs on the remote computer.
-
Process manager: Shows a list of running processes and enables you to stop, pause, and resume them.
-
Service manager: Shows a list of the services installed on the computer and enables you to start and stop them.
-
File transfer: Enables you to send and receive files between your computer and the user computer.
-
Command-line tools: Use commands from the remote control terminal to collect information to enhance investigations, recover data for forensic analysis, and remedy security breaches:
-
delete: Deletes files from the target computer hard disk.
-
dump: Dumps the memory assigned to processes to disk.
-
netinfo: Shows information about network interfaces.
-
pcap: Captures network packets and dumps them to the computer hard disk.
-
ports: Shows processes with open ports on the computer.
-
process: Shows the processes loaded in memory and their modules.
-
url: Shows a history of all the URLs opened from the computer browser.
-
Required permissions
-
To view and modify the remote control settings, the user account must have the Configure remote control permission.
-
To remotely access computers on the network, the user account must have the Remote computer control permission.
For more information about available permissions, see Understanding permissions.
Requirements
The remote control feature is available on Windows, Linux, and macOS computers.
To use the remote access and remote command line tools, the user computer and the network perimeter firewall must allow traffic to and from these URLs and ports:
Remote control settings
To enable remote control for the Windows computers on the network, you must assign a remote control settings profile to the computers you want to access.
-
From the top menu, select Settings. From the side menu, select Remote control. A page opens and shows the existing remote control settings profiles.
-
In the upper-right corner of the page, click Add. The Add settings page opens.
-
In the Name text box, type a name for the settings profile. (Optional) In the Description text box, type a description of the settings profile.
-
Click Save.
-
Click the No recipients selected yet link. Select the computers or computer groups that you want to assign the remote control settings profile to.
-
Enable the toggles for the features you want to be available on the Windows computers:
-
Terminal: Remote access to the console terminal.
-
Process monitor: Remote monitoring of processes.
-
Service monitor: Remote configuration of services.
-
File transfer: Remote transfer of files to or from your computer.
-
-
In the upper-right corner of the page, click Save. The profile is assigned to the target computers and you can establish remote control sessions to them.
Accessing the remote control feature
To start a remote control session from a list, click the context menu of the target computer. Select ![]() Remote control. This option is available in these lists:
Remote control. This option is available in these lists:
-
Licenses
-
Hardware
-
Risks by computer
-
Computer protection status
-
Encryption status
-
Data Control status
-
Computer list
For more information about the lists available in Advanced EDR, see Templates, settings, and views
The remote control feature is also available from the computer details page, which you can open by clicking a row in any of the aforementioned lists.
Remote control tool description
Process manager
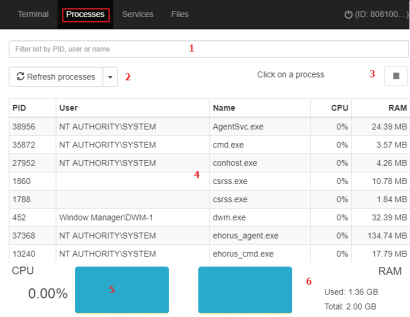
The Process manager shows all processes in the remote computer memory and enables you to search for, stop, and start specific processes remotely. It also provides details on the RAM and CPU used by each process.
It includes these resources:
-
Search tool (1): Filters the list by process ID (PID) or name. You can type only a partial string.
-
Auto refresh (2): Specify the frequency that Advanced EDR refreshes the information in the process list.
-
Stop button (3): Stops a process.
-
Process list (4): Shows the list of processes in the remote computer memory.
-
CPU (5): Shows the percentage of CPU used by all the processes in the remote computer memory. Also, it includes a line chart showing a history of CPU usage since the process manager was opened.
-
Memory (6): Shows the percentage of RAM used by all the processes in the remote computer memory. Also, it includes a line chart showing a history of RAM usage since the process manager was opened.
The process list (4) shows information about each process in the remote computer memory:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
PID |
Process ID. |
|
User |
|
|
Name |
Process name. |
|
CPU |
CPU used by the process. |
|
RAM |
Memory used by the process. |
Service manager
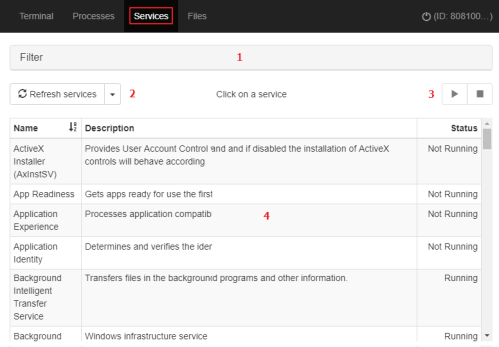
The Service manager shows all services configured on the remote computer and enables you to find specific services to change their status. It includes these resources:
-
Search tool (1): Filters the list by service name or description. You can type only a partial string.
-
Auto refresh (2): Specify the frequency that Advanced EDR refreshes the information in the service list.
-
Service start and stop buttons (3): Stops or starts the selected service.
-
Service list (4): Shows the list of services in the remote computer memory.
The service list (4) shows information about each service configured on the computer:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
Service name. |
|
Description |
Service description. |
|
Status |
Service status:
|
File transfer
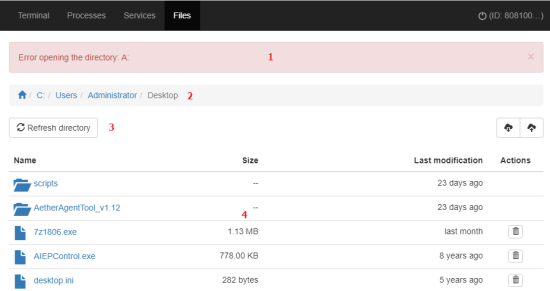
The File manager enables you to transfer files to and from your computer to the remote computer. You can also navigate the file system on the remote computer and delete files. It includes these resources:
-
Message bar (1): If there are errors when you try to get access to the remote computer file system, a message bar shows.
-
Path (2): The file path shows at the top of the window.
-
To change directories, click another drive or folder in the file path or in the Name column.
-
To show the list of devices connected to the computer, click the
icon.
-
-
Auto refresh (3): Specify the frequency that Advanced EDR refreshes the information in the file list.
-
File list (4): Shows the list of files in the selected path (2).
-
Folders
: Click a folder to view the files it contains. The path (2) updates automatically.
-
Delete
 : Deletes the file and removes it from the computer.
: Deletes the file and removes it from the computer.
The file list (4) shows information about each file found on the remote computer:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
File name. |
|
Size |
File size. |
|
Last modified |
Date when the file was last modified. |
|
Actions |
Actions you can take on the file:
|
Remote control terminal
Windows
On the Terminal page of the Remote Control tool, you can run commands compatible with the command interpreter on the remote computer. Also, you can launch programs that generate text output. The remote control terminal runs under the LOCAL_SYSTEM account on the remote computer and is installed here:
|
C:\Program Files (x86)\Panda Security\Panda Aether Agent\Remote access\ |
Linux/macOS
You can open a bash terminal to run compatible commands that generate text output. Commands are run with root permissions on the remote computer.
RT.exe program for Windows computers
Advanced EDR supports rt.exe. This program provides access to a set of tools you can use to respond to security incidents. These tools enable you to recover information to perform a subsequent forensic analysis, and restore devices affected by a security breach to their original state.
You can access the rt.exe program from the remote command line. The program has the following syntax:
|
rt.exe [command] [-h|--help] |
Consider these aspects about the rt.exe program:
-
Each
commandindicates an action to take and each command supports different parameters. -
Wildcards * and ? are not supported.
-
Some parameters allow partial searches that use substrings of characters that represent the start, middle, or end of a string. For example, to search for "malware", you can enter these substrings: "mal" or "ware".
-
If a command supports dumping output to a file, this is specified with
-f. -
To separate multiple items of the same type, enter the pipe character (|).
-
Next, we describe the parameters supported by each command.
Delete command
This command deletes the files specified with the parameters -n, -m, or -s which are in the path indicated by the parameter -p. If the file is in use, the delete command returns an error.
| Short form | Full parameter | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
-h |
--help |
Opens command help. |
|
|
-f |
--force |
Deletes files permanently. |
|
|
-r |
--restore |
Restores selected files from the Recycle Bin. |
Restores files to their original location. |
|
-p |
--path |
Absolute path from the root directory where you want to search for files to delete. The security product only deletes files in the specified path. |
|
|
-n |
--name |
Names of the files you want to delete. |
|
|
-m |
--md5 |
MD5 values of the files you want to delete. |
|
|
-s |
--sha256 |
SHA256 values of the files you want to delete. |
|
Dump command
This command dumps to disk the memory space allocated to a system or user process.
| Short form | Full parameter | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
-h |
--help |
Opens command help. |
|
|
-p |
--pid |
PID of the process to dump. |
For information on how to dump the PID of the process, see Process command. |
|
-s |
--system |
Kernel dump. |
Supported values:
|
|
-f |
--filename |
Name of the file that contains the dump. |
|
|
-z |
--zip |
Stores the dump in a ZIP file. |
|
Netinfo command
Used with the -a parameter, this command shows the settings of the network interfaces installed on the computer.
| Short form | Full parameter | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
-h |
--help |
Opens command help. |
|
|
-a |
--all |
Shows the settings of the network interfaces installed on the computer. |
|
|
-f |
--filename |
Name of the file that contains the data. |
|
|
-z |
--zip |
Stores the information in a ZIP file. |
|
Pcap command
This command captures the network traffic sent and received by the remote computer. Specify the start and end of the capture with the parameters - a start| stop. Packet capture generates temporary files on the computer so there must be sufficient hard disk space. The end result is a PCAP file that can be used directly by the Wireshark/Ethereal program.
| Short form | Full parameter | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
-h |
--help |
Opens command help. |
|
|
-a |
--action |
Executes an action:
|
|
|
-m |
--maxsize |
Maximum size of the packet to capture. |
|
|
-i |
--maxtime |
Maximum capture time. |
|
|
-f |
--filename |
Name of the file that contains the data. |
|
|
-z |
--zip |
Stores the information in a ZIP file. |
|
Ports command
Used with the -a parameter, this command shows the sockets open on the computer and the processes that opened them,
| Short form | Full parameter | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
-h |
--help |
Opens command help. |
|
|
-a |
--all |
Shows all open ports and their associated processes. |
|
|
-p |
--pid |
Filters the results by process PID. |
|
|
-n |
--name |
Filters the results by process name. |
You can type only a partial string. |
|
-f |
--filename |
Name of the file that contains the data. |
|
Process command
Used with the -a parameter, this command shows all processes loaded in the memory of the computer and their modules.
| Short form | Full parameter | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
-h |
--help |
Opens command help. |
|
|
-a |
--all |
Shows all processes loaded in the memory of the computer and their modules. |
|
|
-p |
--pid |
Filters the results by process PID, showing the process modules. |
|
|
-u |
--user |
Shows the processes launched by a user and their modules. |
|
|
-f |
--filename |
Name of the file that contains the data. |
|
Url command
Used with the -a any parameter, this command shows all the URLs accessed by users through the remote computer’s web browser. This command requires that the Advanced EDR web access control feature be enabled.
| Short form | Full parameter | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
-h |
--help |
Opens command help. |
|
|
-a |
--action |
Filters the URL list by the action taken by the web access control feature:
|
|
|
-c |
--count |
Maximum number of URLs to show. |
Default value: unlimited. |
|
-g |
--category |
Filters the URL list by the category assigned by the web access control feature. |
|
|
-b |
--begindate |
Enables you to specify the start date from when to show visited URLs. |
|
|
-e |
--enddate |
Enables you to specify the end date to show visited URLs up to. |
|
|
-n |
--urlpattern |
Filters URLs by substring. |
|
|
-u |
--userpattern |
Filters URLs by user. |
|
|
-f |
--filename |
Name of the file that contains the data. |
|
|
-z |
--zip |
Stores the information in a ZIP file. |
|