Cytomic Orion Architecture
Cytomic Orion is an advanced threat hunting service that integrates with the different tools used by corporate SOCs to perform these tasks:
-
Triage/filter indicators.
-
Investigate threats.
-
Set containment and response policies.
-
Report detected malicious activity and the actions performed to mitigate its effects.
To do that, Cytomic Orion analyzes all the information collected by Cytomic EDR: the events and actions carried out by the processes run on workstations and servers are sent to the cloud and enriched with context and security information to generate telemetry. This telemetry is interpreted by Cytomic Orion to generate indicators that SOC technicians investigate, searching for malicious activity.
Below is a diagram of the different modules that make up Cytomic Orion, as well as the actors and data sources that interact with the environment. Additionally, there is an introduction to the concepts most frequently used in this User Guide.
The Cytomic Orion architecture is divided into three large groups:
-
SOC/MSSP/MDR staff.
-
Platform processes and technologies.
-
Intelligence, integration, and external data sources.
SOC/MSSP/MDR Staff
In mid-to-large-sized SOCs, technical staff are specialized and organized into tiers according to their skill sets:
-
Tier 1: Analysts performing indicator triage. They check and catalog the hypotheses generated by Cytomic Orion and create investigations that group similar indicators to assign them to Tier 2 and Tier 3 technicians, who analyze them in more depth. Additionally, Tier 1 technicians rule out false hypotheses that correspond to normal process operations. As such, they act as a filter that prevents overloading higher tiers.
-
Tier 2: Analysts who receive the investigations generated by Tier 1 which are likely to pose a threat to the organization. This tier is responsible for investigating indicators to identify genuine intrusion attempts, assessing the resulting damages, and setting relevant remediation and containment methods.
-
Tier 3: Top-level security analysts who develop new hypotheses using different investigation methods based on external information, such as third-party security bulletins, CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities & Exposures), portals and web pages specialized in security, etc. They do not require the indicator triage performed in Tier 1 in order to perform their tasks,
-
SOC Manager: Responsible for coordinating analyst activity, reassigning investigations, allocating resources and time to priority clients, and assessing the performance and results of completed investigations.
Platform Processes and Technologies
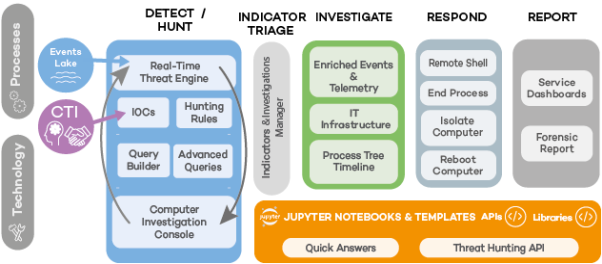
| Process | Technology | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Detection and searches |
CTI (Cyber Threat Intelligence) |
Open-source platform that centralizes and stores security intelligence about recent malware. It supports investigations into cyber crime and cyber espionage. |
|
Data lake |
Data source used by Cytomic Orion to execute hunting processes and retrospective analyses. It contains all telemetry collected from computers in the organization as a result of monitoring the processes run on all workstations and servers on the company network. The retention time for the telemetry stored in the data lake is one year. |
|
|
Real-time cyberattack radar |
Checks the data lake automatically and in real time, searching for suspicious event patterns that could indicate a cyberattack. |
|
|
Hunting rules |
Describe the behavior patterns that the cyberattack radar looks for in the telemetry data flow generated by the processes executed on the client’s computers. See Indicators and Hunting Rules and Manage Hunting Rules. |
|
|
IOCs |
Industry standard for describing conditions that can compromise the security of organizations. Despite being a similar concept to the signature file used by malware protection tools, IOCs use an open format that enables sharing and exchange. The cyberattack radar supports IOCs to search for patterns in real time. |
|
|
Wizard-guided queries |
Build queries in a simple, guided way to retrieve tabulated information from the data lake. See Advanced SQL Query Module. |
|
|
Advanced queries |
Create complex SQL queries. See Advanced SQL Query Module. |
|
|
Investigation console |
Enables a retrospective analysis of the processes run on workstations and servers to get more in-depth data about the conditions that triggered the indicator generated by the real-time cyberattack radar. See Indicator Analysis Using the Investigation Console. |
|
|
Indicator triage |
Manual filtering by Tier 1 analysts of the indicators generated by the cyberattack radar. Its purpose is to distinguish indicators corresponding to real attacks from false positives. This prevents task overload at Tier 2, directing analysts’ attention to the cases that pose an actual threat to the organization. |
|
|
Analysis |
This includes all the features of the investigation console, the graphs, and the resources implemented in the agent installed on the company IT devices. |
|
|
Process tree |
Shoes the parent-child relationships of the processes run on the computers on the IT network. See Graphs. |
|
|
Timeline |
Shows all occurred events, sorted by time stamp to help analysts view the progression of attacks. |
|
|
Enriched event list |
Shows the complete list of all events occurred and enriched with Cytomic security intelligence. See Indicator Analysis Using the Investigation Console. |
|
|
IT infrastructure |
Complete access to the status of resources and processes on the computers within the company IT infrastructure. See IT Infrastructure Investigation with OSQuery. |
|
|
Incident response |
Tools for remotely resolving security breaches and retrieving information to be used in the forensic analysis of compromised computers. See Response Tools. |
|
|
Jupyter Notebooks |
They automate retrospective analyses, generate reports, and enable analysts to share hunting techniques. See Investigations with Notebooks. |
|
|
Quick answers |
Small reusable code snippets that function independently and resolve specific issues arising frequently in analysts’ daily routines. See Response Tools. |
|
|
Templates |
Predefined notebooks published by Cytomic or by clients to be shared and used as a base by analysts in the automation of hunting tasks. See Template Management. |
|
Intelligence and Data Sources

| Data source | Description |
|---|---|
|
Query library |
Speeds up and facilitates analysts’ hunting tasks. It is built and maintained by the Cytomic team of threat hunters and SOC analysts using Cytomic Orion. See Investigate the Event Flow. |
|
Threat hunting library |
Access the data lake from notebooks and speed up analysis procedures. For more information about this library, go to https://info.cytomicmodel.com/resources/help/ORION/es/threathuntingAPI/index.htm. |
|
IOC API |
Enables the use of external sources of security intelligence to import new indicators of compromise, thereby extending the analysis capabilities of hunting rules. See IOC API. |
|
Indicator API |
Provides integration with ticketing platforms to automate and improve the monitoring of the incidents detected by Cytomic Orion. See Indicator API. |
|
Knowledge API |
Share, with third parties, extended information about the files seen on the client’s IT network and the computers that store them. See Knowledge API. |
|
Incident response API |
Allows third-party applications or applications developed by the SOC to isolate, deisolate, and restart computers from the client's network that are at risk of a cyberattack. See Response API. |
|
OSQuery access API |
Gets detailed information about the status of resources and processes executed on a user’s computer. See OSQuery Access API |
|
Notebook templates |
The Cytomic team of threat hunters develops and maintains a library of notebook templates that automate the most complex retrospective analyses and are used as a base by SOC analysts for their own developments. |
|
Quick answers |
The Cytomic team of threat hunters develops and maintains a library of reusable code snippets for resolving very specific problems. These snippets can be used as a base by SOC analysts to develop more complex notebooks. |
Data Lake and Process Monitoring
Cytomic Orion relies on the probes installed on workstations and servers to continually monitor the running of all processes loaded into computers’ RAM, regardless of whether these have been previously classified as goodware, system processes, non-classified (unknown) processes, malware, or PUPs. Any process classified as goodware which has been compromised (for example, through exploits that use a vulnerability detected in the process) is monitored and its telemetry is sent to the data lake This way, analysts can investigate and check the sequence that led to the exploitation of that vulnerability and its effects on the compromised process to organize the response tasks considered necessary.
Likewise, programs classified as suspicious by the heuristic engines of the security solution are also monitored, and their telemetry is sent to an analyst to determine whether their behavior is legitimate or whether they show a sequence of actions that can be interpreted as dangerous and harmful to an organization.